
Overview:
From the groundbreaking Human Genome Project, a monumental and globally coordinated endeavor conducted from 1990–2003 that marked the inception of sequencing the human genome, to the establishment of Genome Valley, an expansive 2,000-acre high-tech business district in Hyderabad, India, dedicated to advancing life sciences research and development (R&D), the trajectory of genomics has been transformative. Genomics, with its diverse technologies like Optical Genome Mapping, DNA Sequencing, Genome Detective, and extensive genome libraries, has not only revolutionized precise medication and healthcare solutions but has also charted a course of innovation in various sectors beyond medicine. These innovations extend to agriculture, energy, and cattle farming, showcasing the expansive reach and potential impact of genomics across diverse domains. Immerse yourself in this enlightening article of the multifaceted aspects of genomics to delve deeper into the multifaceted world of genomics and its far-reaching implications across critical sectors.
Contents
- What is a Genome
- How a Genome Looks Like
- How Whole Genome Sequencing is Redefining Bioresearch
- Is Whole Genome Sequencing Different from DNA Profiling
- How a Genomics Market Ecosystem is Structured
- The General Aspect – Key 6-Ways Genomics Impacts Our Day-to-day Life Positively
- The Market Aspect – Global Market Landscape of Genomics
- The Technological Aspect – The Role of AI, ML, and Data Analytics in Assisting Genomics
- The Economic Aspect – Key Developments in Genomics by the Top 5 Economies
What is a Genome:
The genome serves as the comprehensive assembly of DNA instructions within a cell. It encompasses all the genetic material, both coding and non-coding, within an organism. Every living entity possesses its unique genome, a reservoir of biological information crucial for constructing and sustaining the organism throughout its lifespan. Within the genome resides the intricate blueprint that outlines the developmental journey of an organism, orchestrating its progression from a solitary cell into a fully developed entity.
This intricate genetic map not only directs the growth of the organism but also imparts vital instructions to its organs, directing them in their specific functions. Furthermore, the genome plays a critical role in composing repair processes within the organs, intervening and restoring functionality when damage occurs. In essence, the genome is the foundational guidebook of life (of both animal and plant), holding the key to the genesis, maturation, and maintenance of an organism.
How a Genome Looks Like:
The genome is composed of deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA, an immense molecule resembling a lengthy, twisted ladder. If we were to stretch all the DNA contained within a single human cell, it would create a strand approximately six feet long, representing a code of about six billion letters. Remarkably, this extensive structure is intricately packed within the nucleus of a cell, an organizational feat that condenses it to a highly structured form. The nucleus is so tiny that it necessitates observation through specialized microscopes for visualization.
How Whole Genome Sequencing is Redefining Bioresearch:
Whole genome sequencing is a highly advanced genetic analysis technique that allows for the simultaneous examination of tens of thousands of genes within an organism’s genetic makeup. It provides a swift and comprehensive assessment, facilitating the rapid detection of a wide array of genetic anomalies. This extensive analysis encompasses the sequencing of all the chromosomal DNA within an organism, including the mitochondrial DNA (or chloroplast DNA for plants). The resulting data is invaluable in tailoring and determining the most effective course of care for the individual based on their unique genetic profile.
Is Whole Genome Sequencing Different from DNA Profiling:
Absolutely yes! Whole Genome Sequencing goes beyond the capabilities of DNA profiling or genetic fingerprinting. While the latter can determine the likelihood that genetic material originates from a particular individual or group, Whole Genome Sequencing offers an added dimension by providing comprehensive insights into genetic relationships, origins, and even susceptibility to specific diseases. It furnishes a deeper understanding of an individual’s genetic landscape, aiding in a more thorough analysis and interpretation of their genetic makeup.
How a Genomics Market Ecosystem is Structured:
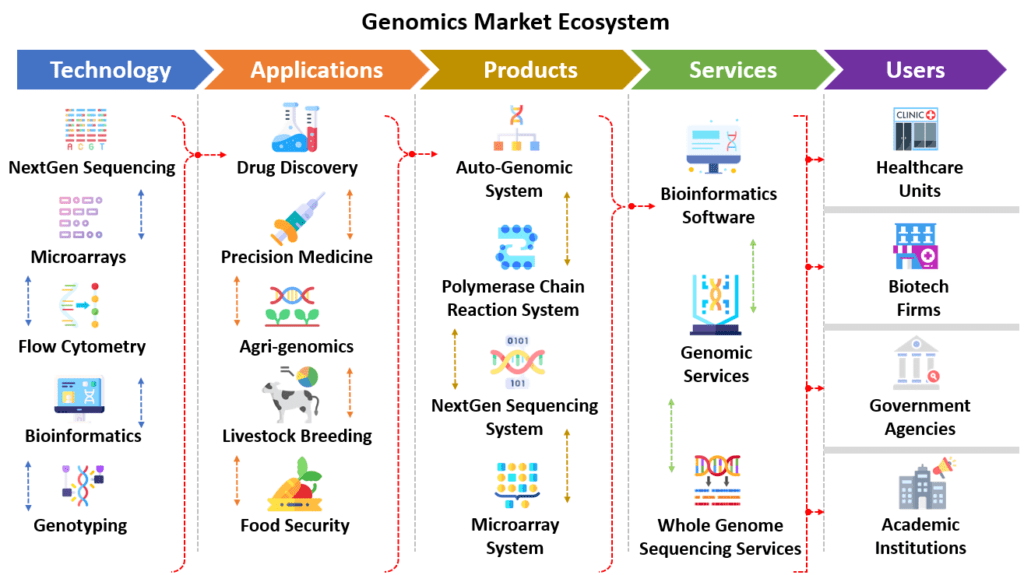
The General Aspect – Key 6-Ways Genomics Impacts Our Day-to-day Life Positively:
As technology advances and our understanding of the genome deepens, numerous aspects of our daily lives are being significantly influenced by genomic information and related technologies. From healthcare and medicine to agriculture, energy, and beyond, genomics is playing an increasingly crucial role in shaping and enhancing various domains of our lives:
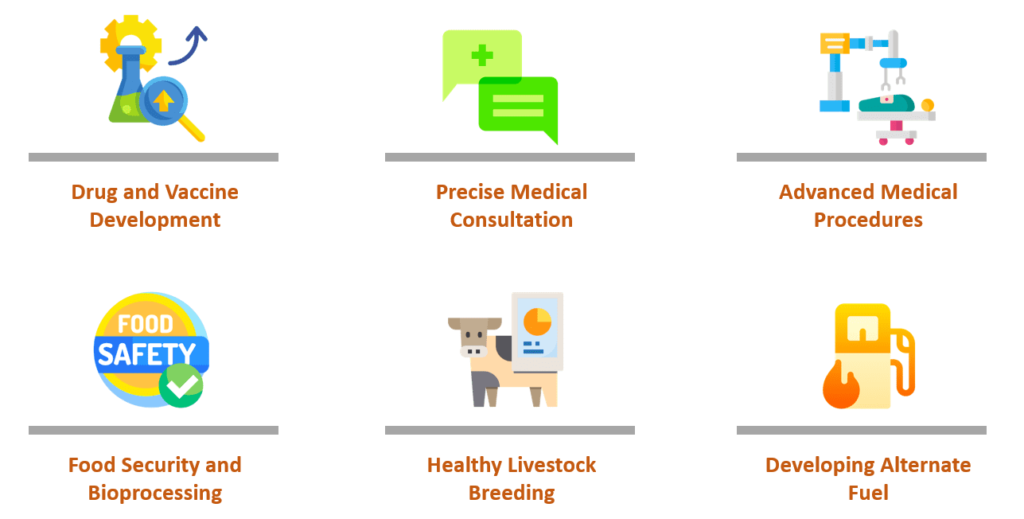
1. Drug and Vaccine Development
The insights derived from the human genome have unveiled molecular targets for therapeutics, especially in the treatment of genetic diseases. The integration of genetics and genomics into drug development has yielded numerous clinical triumphs, notably advancements in cancer therapeutics and the rapid development of effective COVID-19 vaccines.
Moreover, the routine sequencing of genomes in clinical research has significantly increased the availability of publicly accessible human genomes. Analyzing these genomes in large volumes has paved the way for substantial biomedical discoveries aimed at enhancing human health and well-being
2. Precise Medical Consultation (Pharmacogenomics)
Genomic information plays a pivotal role in tailoring treatments for patients. Genetic screening tests are instrumental in identifying disease-causing gene variants, determining predisposition to chronic conditions like hereditary cancer and cardiovascular diseases, or predicting potential disorders. Doctors can leverage an individual’s genetic data to make informed decisions about the most effective drug and appropriate dosage, streamlining the treatment process with greater efficiency and accuracy.
3. Advanced Medical Procedures (Gene Therapy)
Gene therapy, though promising, is in its nascent phase. The goal of gene therapy is to alter an individual’s genes, either by replacing or deactivating disease-causing genes, or by introducing new or modified genes into the body. This approach holds potential for treating and potentially curing diseases by addressing the root genetic causes.
4. Food Security and Bioprocessing
Big data genomics research has the potential to enhance global food security. Through processes like genome sequencing and analysis of various crops, it’s possible to improve crop yields even in conditions of pest resistance and adverse environmental factors. This research facilitates the development of crops that are resistant to diseases, insects, and drought, ultimately optimizing them for bioenergy production and ensuring a more sustainable agricultural future.
5. Healthy Livestock Breeding
Genome sequencing plays a pivotal role in advancing cattle farming by accelerating and refining selective breeding techniques. By leveraging genomics, it’s possible to develop a healthier breed of farm animals that exhibit enhanced productivity, resistance to diseases, and increased meat production. This ultimately leads to a more efficient and profitable cattle farming industry.
6. Developing Alternate Fuel
Sugarcane stands as a highly sustainable energy crop, offering remarkable yields in terms of cultivated plant tonnage. Its efficiency in producing sugar, bioethanol, and bioelectricity positions it as a viable eco-friendly substitute for petroleum. Geneticists specializing in sugarcane have meticulously examined and unraveled its intricate genome using an array of genomic tools. This comprehensive understanding has paved the way for optimizing its utilization as an alternative and greener source of fuel.
The Market Aspect – Global Market Landscape of Genomics:
As per a report, The global genomics market is poised for substantial growth, projected to surge from USD 33.2 Billion in 2022 to a staggering USD 411.3 Billion by 2030, showcasing a remarkable compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 19.4% during 2023-2030. North America is anticipated to dominate with the largest market share, while the APAC market is expected to witness the highest growth rate over this period.
Potential Drivers
1. Escalating incidences of rare genetic diseases and life-threatening conditions like cancer on a global scale have prompted a surge in government funding for genomics initiatives.
2. The dedicated exploration of specialized bioprocessing domains, notably the human genome, has paved the way for personalized healthcare and medicinal advancements within genomics.
3. The burgeoning demand for efficient clinical diagnoses is propelling research in genomics-based solutions, driving significant investments in R&D by biopharmaceutical enterprises.
4. The continuous advancement of Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS), particularly in its widespread utilization in cancer research, is a key driver propelling the global genomics market.
5. The extensive application of cutting-edge techniques like whole-genome sequencing, genome diversity analysis, metagenomics, epigenetics, identification of non-coding RNAs and protein-binding sites, along with gene-expression profiling via RNA sequencing, is broadening the horizons of genomics research.
Potential Barriers
1. Market growth and expansion may be impeded by a shortage of professionals proficient in genetics and subject matter experts, potentially leading to a delay in market development.
2. The high cost associated with genomic research equipment poses a significant challenge, making genome sequencing an expensive endeavor. The sequencing expenses are estimated to exceed USD 1000/genome in a single laboratory.
3. The substantial volume of sequenced data stored in the cloud presents consistent compliance and security concerns. The escalating risk of data breaches from the cloud further exacerbates this challenge.
4. Managing patient data proves to be intricate, given that a single patient’s genetic examination can yield about 1 terabyte of data in a single visit. The extensive amount of new data generated from pre-diagnosis, diagnosis, and treatment, including lab imaging data, clinical observations, tissue biopsy, and other morphologic data, compounds the complexity of data management.
The Technological Aspect – The Role of AI, ML, and Data Analytics in Assisting Genomics:
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Artificial Intelligence driven advancements in genomics hardware and software have significantly expedited the genomic sequencing process, enhancing speed, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness. High-throughput sequencers integrated with AI algorithms can efficiently process vast quantities of genomic data, empowering researchers to conduct genome analyses with greater efficiency. Moreover, AI augments the potential of microarray technologies, refining their sensitivity and specificity for gene expression analysis, thus advancing diagnostics, precision medicine, and drug discovery.
According to a report, the integration of artificial intelligence in genomics is projected to evolve into a USD 12.5 Billion market by 2032, with a notable compounded annual growth rate (CAGR) of 39.2% expected from 2023 to 2032. This surge is primarily driven by the increasing emphasis on reducing turnaround time in drug discovery processes.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning algorithms play a pivotal role in advancing the analysis of genomic data. They facilitate the identification of intricate patterns, crucial biomarkers, and potential therapeutic targets within vast genomic datasets. Through machine learning techniques, predictive models are crafted, enabling the assessment of an individual’s disease susceptibility by analyzing their unique genomic profile. These models provide valuable insights for healthcare professionals, aiding in the interpretation of complex genomic data and empowering them to make informed decisions regarding personalized treatment strategies.
Big Data Analytics
Big data analytics has revolutionized DNA sequencing by leveraging powerful computational and statistical methods to decode and comprehend vast amounts of genomic data. By comparing and analyzing extensive datasets, it uncovers hidden patterns, unknown correlations, and valuable insights in genomics.
An illustrative example is the Human Genome Project, a monumental effort that provided a complete draft of the 3 billion letters constituting one human genome. These letters, symbolized by the four nucleotides Adenine(A), Cytosine(C), Guanine(G), and Thymine(T), make up the DNA. Remarkably, nearly every individual shares the same 3 billion DNA base pairs, demonstrating a 99.9% genetic similarity among humans. However, within the remaining 0.1%, slight differences can lead to various disorders and diseases. Big data analytics plays a critical role in analyzing this critical 0.1% of DNA data.
Notably, the data for a single genome amounts to approximately 200 gigabytes. In the early stages of genomic research, it took 14 years and a staggering cost of USD 2.2 billion, with the collaborative efforts of thousands of scientists, to sequence a single genome.
The Economic Aspect – Key Developments in Genomics by the Top 5 Economies:
United States
1. Agilent Technologies, in response to the burgeoning USD 1 billion market and a robust demand for its high-quality active pharmaceutical ingredients (API), has outlined an ambitious plan to invest approximately USD 725 million. This investment aims to double the manufacturing capacity dedicated to therapeutic nucleic acids, positioning the company to meet the escalating demands of this rapidly expanding sector. (2023)
2. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) in the United States has unveiled an ambitious plan to allocate approximately USD 5.8 million over the upcoming five years. This funding will be channeled towards the establishment of an educational hub focused on advancing computational genomics and data science. The initiative is set to significantly bolster research and knowledge dissemination in these critical domains, fostering advancements at the intersection of genomics and data science. (2023)
3. In a strategic move, Eli Lilly and Company, in the early months of 2022, inaugurated the Lilly Institute for Genetic Medicine. Simultaneously, the company committed a substantial investment, amounting to approximately USD 700 million. This funding injection is slated to underpin the creation of a cutting-edge facility, strategically situated in the Boston Seaport area. The institute’s focus on genetic medicine aligns with the broader industry’s concerted efforts to leverage genetics for transformative healthcare solutions.
China
1. China has demonstrated a steadfast commitment to advancing genetic engineering research, striving to secure a prominent position on the global stage in this domain. As of the current year, 2023, the cumulative investment in the gene therapy field in China has soared beyond a substantial USD 3.3 billion. Forecasts indicate an even more ambitious trajectory, anticipating that by the year 2025, gene therapy investments in China will surge to an estimated USD 17.9 billion, underscoring the nation’s strategic and financial dedication to genetic research and therapeutic advancements.
2. Gene editing has garnered a prominent position on the national strategic agenda, being explicitly outlined as a critical objective in both the 13th and 14th Five-Year Plans, as well as in the visionary blueprint for the year 2035. This underscores the significant focus and prioritization accorded to gene editing technologies in driving scientific and technological advancement in the country’s long-term vision.
3. In a pivotal move during June 2023, China’s Ministry of Science and Technology introduced crucial amendments to the Administrative Regulations on Human Genetic Resources (HGR). These alterations were aimed at streamlining the disclosure and sharing of HGR data, reinforcing data protection and national security measures, defining the parameters of ‘Foreign Entities’, easing intellectual property ownership and data sharing responsibilities, refining the oversight of HGR-associated undertakings, and fortifying legal enforcement mechanisms.
Japan
1. Omron Ventures, a prominent corporate venture capital firm, demonstrated its interest in the genomics realm by investing in Eagle Genomics, a leading TechBio platform provider focused on advancing genomics platforms and technologies. (2023)
2. Riken Genesis, a prominent gene research firm, joined forces with the US-based C2i Genomics to advance the commercialization of its C2intelligence cloud-based platform and the C2inform MRD test. This collaboration is set to revolutionize pharmaceutical and clinical research. C2i Genomics brings its cutting-edge technology into play, enabling precise monitoring of cancer tumor burden through ultra-sensitive whole genome sequencing (WGS), thus propelling personalized medicine and expediting drug development. (2023)
Germany
1. Four esteemed German university medical centers, in partnership with the UK-based Oxford Nanopore Technologies, have initiated the Clinical Long-read Genome Initiative (lonGER). Over a span of two years, the initiative aims to meticulously analyze approximately 1,000 samples. The overarching goal is to pave the way for the clinical integration and adoption of nanopore sequencing, a pivotal aspect of whole-genome sequencing. (2023)
India
1. The Reliance Industries Group is set to embark on significant investments in genetic mapping projects and associated research. Their aim is to provide an affordable genome sequencing test solution priced at just USD 145. This initiative will be facilitated through their acquired entity, Strand Life Sciences. (2023)
2. Lord’s Mark Microbiotech, a prominent biotech firm, is gearing up to broaden its genome testing services in India. Their upcoming venture involves the establishment of the first online lab dedicated to genome testing, showcasing their commitment to advancing genetic diagnostics and research. (2023)
3. Illumina, a leading global DNA sequencing research firm, has made significant strides in India by establishing a solution center. This initiative aims to enhance access to genomics within the local community, demonstrating Illumina’s dedication to advancing genomics research and its applications in the Indian context. (2023)











