
Overview:
While the concept of digital healthcare may sound relatively recent, its roots extend far into the past. For example, the use of medical images and telemedicine has been prevalent for over seven decades, and health monitoring devices gained popularity as far back as the 1960s. Over the years, the digital healthcare sector has experienced significant evolution, with a particularly transformative shift occurring during and after the COVID-19 pandemic. The successful implementation of contactless healthcare delivery at people’s doorsteps marked a pivotal moment.
The future of digital healthcare holds great promise, yet it is not without its challenges and pitfalls. Several critical factors and mistakes pose obstacles to achieving a seamless growth trajectory.
Contents:
- What is Digital Healthcare
- The messes in the Digital Healthcare Ecosystem
- Details of the Potential Messes that Derail Digital Healthcare
- Wrapping Up
What is Digital Healthcare:
Digital healthcare represents a unique healthcare delivery system in which patients receive consultations and medication through a range of digital technologies and touchpoints, including smartphone apps, wearable devices, and telehealth platforms supported by technologies such as Artificial Intelligence or Internet of Things. This approach enhances accessibility, affordability, and sustainability throughout the entire healthcare process.
The Potential Messes that Derail Digital Healthcare:
While the digital healthcare ecosystem features interconnected links to ensure the seamless flow of execution, it also harbors potential disruptive forces at each node that can impede the smooth progression of digital healthcare procedures. Let’s explore these factors further to gain a deeper understanding:
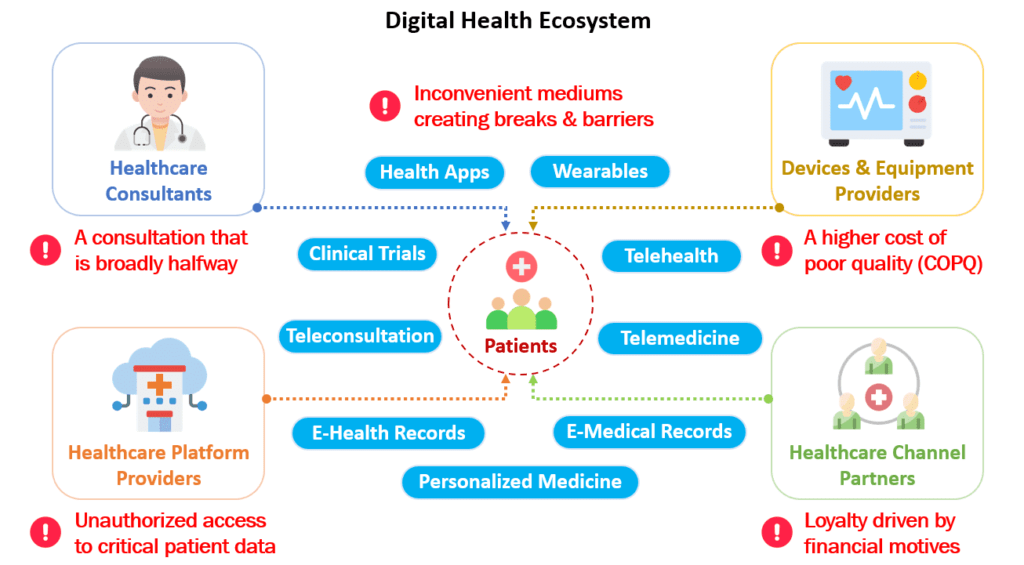
1. A Consultation that is Broadly Halfway
The primary and most crucial node within the digital healthcare ecosystem is the healthcare provider, upon whom patients heavily rely. These providers, often virtual doctors accessible through mobile apps or websites, play a pivotal role in addressing patients’ key health concerns.
In contrast to traditional face-to-face consultations, where patients benefit from direct interactions with physicians who can observe physical cues and conduct hands-on examinations, virtual doctors in the digital healthcare ecosystem primarily rely on verbal communication to listen and provide recommendations. While this approach can be effective in some cases, it often falls short. Patients may struggle to convey their feelings or express health-related facial cues, limiting the effectiveness of remote consultations.
Moreover, trust can be a significant concern in virtual healthcare interactions. Patients may question the ability of virtual doctors to effectively address their health issues. Some virtual doctors may lack hands-on clinical experience and may have limited educational backgrounds, which further contributes to these trust issues.
2. Inconvenient Mediums Creating Breaks & Barriers
In the digital healthcare ecosystem, a significant portion of patients remains less technologically adept. Many individuals exhibit reluctance to embrace information and communication technologies, which form the bedrock of the virtual healthcare ecosystem, including telemedicine. This resistance engenders a set of challenges that affect both patients and healthcare providers. These challenges encompass issues such as audio and video quality, internet connectivity, software accessibility, diagnostic accuracy in telehealth, and even concerns related to identity theft.
3. A Higher Cost of Poor Quality (COPQ)
Medical device end-users depend on safe and effective devices to monitor and manage their health regularly. For these users, the cost of poor quality (COPQ) can have severe consequences. In an industry often characterized by lenient regulatory norms, concerns regarding quality frequently arise, encompassing aspects like design, software, and the use of non-conforming materials and components.
Issues can escalate if a medical device is manufactured and subsequently necessitates a recall. COPQ can lead to costly delays, potentially requiring product recalls and exposing end-users to grievances, injuries, or even fatal outcomes. Beyond the immediate impact, poor quality and product recalls pose a significant risk to a company’s reputation, costing the medical device industry billions each year.
4. Unauthorized Access to Critical Patient Data
Healthcare platform providers inevitably gain access to critical patient data, information that patients rightfully want to keep confidential. Within the digital healthcare ecosystem, the paramount objective is to ensure the availability, confidentiality, and integrity of this vital patient data. A breach in security could not only jeopardize patient privacy but also endanger lives.
To address these concerns, many healthcare platform providers pledge to adhere to stringent regulations, such as the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), assuring patients that their data is handled with the utmost care and security. Nevertheless, the healthcare sector remains a prime target for cyberattacks, with attackers attempting to infiltrate data repositories and launching ransomware attacks to seize control of systems until their demands are met.
Typically, healthcare platform providers source patient details from healthcare equipment, which communicates invaluable patient information through their platforms. However, the rising threat of medical device hijacking, known as ‘med-jacking,’ poses an increasingly significant risk to patient data security.
5. Loyalty Driven by Financial Motives
The digital healthcare ecosystem relies heavily on key channel partners, including independent dealers, distributors, resellers, value-added resellers (VARs), and original equipment manufacturers (OEMs). These partners play a vital role in meeting the doorstep requirements of virtual patients. They act as the crucial link connecting the healthcare industry with end-users, ensuring that the market’s core needs are met promptly. Further, channel partners contribute significantly to the ecosystem by expediting product launches, ensuring swift product delivery to customers, enhancing competitive advantages, and leveraging existing customer networks. However, it’s essential to acknowledge that their actions may sometimes be driven by hidden motives and incentives.
In practice, channel partners may prioritize products with higher profit margins, such as certain drugs or equipment, over others. Virtual patients, known for their ease of purchasing drugs and equipment, are often targeted with heavily marketed and discounted offerings. As a result, channel partners may promote products that align with their interests, potentially placing the well-being of virtual patients at a lower priority.
Wrapping Up:
In conclusion, the digital healthcare ecosystem holds immense promise for transforming the way we access and receive medical care. However, beneath its shiny exterior, it conceals a range of hidden encounters that demand our attention and collective efforts. From issues related to patient tech literacy and data security to the complex dynamics among channel partners, these challenges underscore the need for a holistic approach to digital healthcare innovation. By acknowledging and addressing these challenges head-on, we can pave the way for a more equitable, accessible, and secure digital healthcare landscape that truly puts patients’ well-being at the forefront. Only then can we fully unlock the potential of this transformative healthcare paradigm.












2 thoughts on “Unearthing the 5 Hidden Messes Impacting Digital Healthcare Ecosystem”