
Overview:
It would be unjust to assume that any one of us has not encountered the frustration of poor network speed quality on a wireless telephone network. Virtually all of us have experienced the inconvenience of network disruptions and delay, whether we find ourselves amidst a bustling city or in a secluded remote area. This persistent issue remained unresolved until the advent of 5G technology, which emerged as a transformative solution, effectively addressing a myriad of network speed-related challenges. Notably, 5G’s introduction brought about substantial enhancements such as heightened data throughput and remarkably low latency.
In the forthcoming article, our focus will delve into the intricacies of 5G network technology. We will not only explore its distinguishing features that set it apart from preceding alternatives, but we will also gain insight into its distinctive positioning within the technological landscape. Additionally, we will shed light on the prominent applications and use cases along with entities that are driving advancements in this field and examine noteworthy global developments that have unfolded as a result of this cutting-edge technology.
Contents:
- What is 5G Network Technology
- A Glimpse into the Composition of the 5G Ecosystem
- How 5G is Different from Earlier Network Technologies
- How 5G is Related to 3GPP
- The 5G Market Landscape
- What 5G Offers to a Common Man
- Key Application Areas of 5G
- Key Benefits it Offers to the Industry
- Availability of 5G Around the World
- Key Developments in 5G in the Top-5 Economies
What is 5G Network Technology:
5G represents the fifth evolution in the progression of mobile network technology. Preceded by the advancements of 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G, 5G emerges as a milestone in connectivity innovation. Distinguishing itself as the most robust and adaptable mobile network iteration to date, 5G claims to have a remarkable capacity to establish connections with a diverse array of 5G-enabled devices, machinery, and even mobile entities in motion.
Prior to the emergence of 5G, the data throughput capabilities of preceding generations were constrained, culminating in an inability to support seamless activities such as teleconferencing or uninterrupted streaming of online videos. The prevalent issues of subpar audio-video quality and persistent buffering during online activities ultimately affected the user experience. In direct response, 5G embarked on a mission to redefine the individual’s mobile encounter by introducing a suite of enhancements.
At its core, 5G introduces the potential for multi-Gbps peak data speeds, setting the stage for an era of heightened connectivity. This newfound velocity is instrumental in mitigating latency to an ultra-low level, thereby enhancing the network’s dependability for critical applications. Through these commitments, 5G emerges not just as an incremental advancement, but as a transformative force poised to reshape the way we interact with mobile technology.
A Glimpse into the Composition of the 5G Ecosystem:
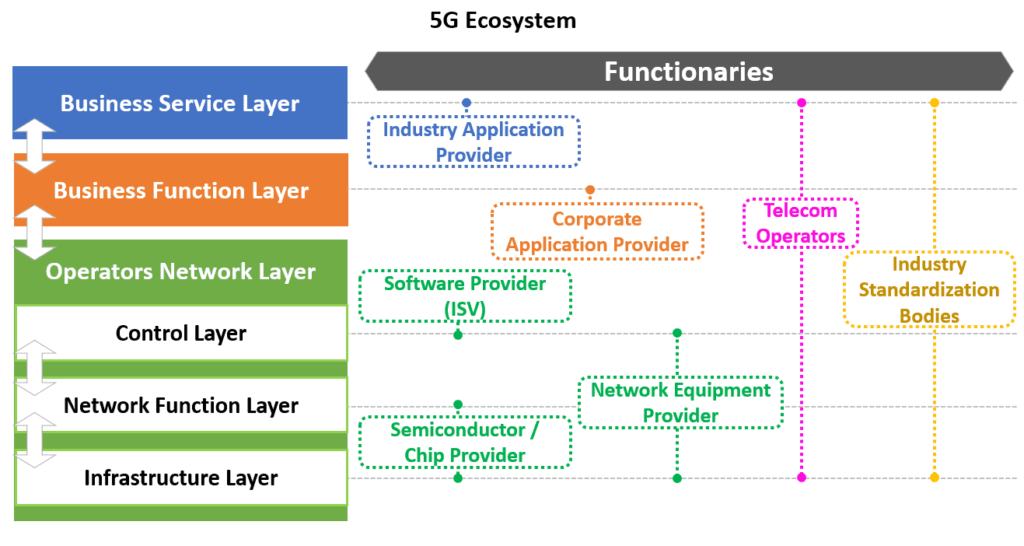
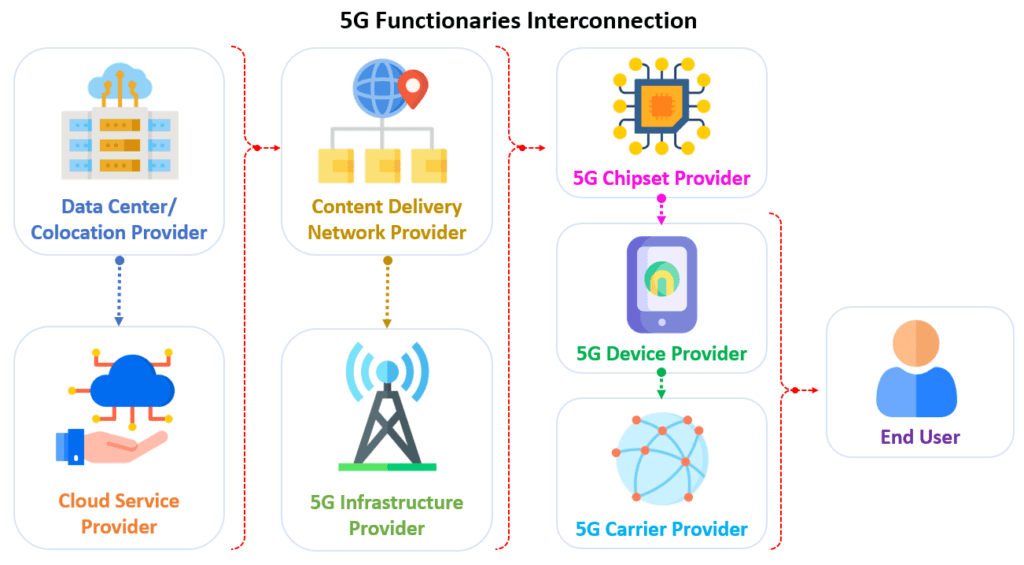
How 5G is Different from Earlier Network Technologies:
| Particulars | 1G | 2G | 3G | 4G | 5G |
| Introduction | 1979 | 1991 | 2000 | 2008 | 2016 |
| Deployment | 1980 | 1991 | 2001 | 2009 | 2019 |
| Concept | Wireless | Wireless | Wireless | Wireless | Wireless |
| Standards | AMPS, TACS | GSM, EDGE/GPRS – 2.5G | WCDMA, HSPA(+) | LTE, WiMAX | MIMO, Milli-meter Wave |
| Access Mode | FDMA | TDMA, CDMA | CDMA, UMTS | CDMA | OFDM, BDMA, 5G NR Air Interface |
| Encoding | Analog (Partially Digital) | Digital | Digital | Digital | Digital |
| Frequency | 150MHz / 900MHz | 1.8GHz (900MHz) | 1.6 – 2.0 GHz | 2 – 8 GHz | 1 GHz – 6 GHz |
| Bandwidth | 30 KHz | 900MHz (25MHz) | 100 MHz | 100 MHz | 30 GHz to 300 GHz |
| Network Switching | Circuit Switching | Circuit Switching for Voice, Packet Switching for Data | Packet Switching (Mostly, except air interference) | Packet Switching | Packet Switching |
| Data Rate (at Ideal Network State) | 2.4 Kbps | ~20 to 64 Kbps | 144 kbps to 10 Mbps | 2 Mbps to 150 Mbps | 200 Mbps To 20 Gbps |
| Network Core | PSTN | PSTN | Packet Network | Internet | Internet |
| USP | Wireless Connectivity | SMS, MMS, Internet Access, SIM Cards | High Data Security, International Roaming | Global Mobility, High-Speed Network Hand-off | Extremely High Throughput, Low Latency |
| Applications | Voice Call | Voice Call, Short Messages (Replacing Pagers) | Mobile TV, GPS, Video Call | Mobile TV, High-speed App Enabled | HD Video Streaming, Remote Driving/ Medical Procedures |
How 5G is Related to 3GPP:
3GPP, short for the 3rd Generation Partnership Project, is a collaborative effort uniting seven major telecommunications standard development organizations: ARIB, ATIS, CCSA, ETSI, TSDSI, TTA, and TTC. Together, these partners have been instrumental in providing comprehensive global reports and specifications for 3G UMTS, 4G LTE, and the groundbreaking 5G technologies.
With a focus ranging from air interface to service layer, 3GPP has played a crucial role in driving essential innovations within the realm of 5G design. Its members include a diverse range of stakeholders, from 5G infrastructure vendors and component manufacturers to mobile network operators and vertical service providers. This collaborative approach ensures a multifaceted perspective, contributing to the evolution of telecommunications and the transformative potential of modern mobile technologies.
The 5G Market Landscape:
As per a report, in 2022, the global 5G technology market achieved a valuation of USD 121.2 Billion. Projections indicate a remarkable growth trajectory, with expectations set for the market to surge to a staggering USD 1799.8 Billion by 2030. This expansion is slated to occur at an impressive compounded annual growth rate of 40.2% from 2022 to 2030.
The impetus behind this upward trajectory is driven by significant advancements in regions like North America, Europe, and Southeast Asian countries. These regions are anticipated to serve as pivotal catalysts for the forthcoming evolution of the 5G market.
Moreover, IHS forecasts present a compelling perspective on the transformative impact of 5G. By the year 2035, it is anticipated that 5G technology will not only catalyze a global economic sales volume amounting to USD 13.1 Trillion across diverse industries, but it will also facilitate the creation of up to 22.8 million jobs directly attributable to the capabilities of 5G-enabled technologies. These projections underpin the profound potential that 5G holds, both as a technological enabler and as a driving force behind substantial economic and employment growth.
What 5G Offers to a Common Man:
The transformative potential of 5G extends to various aspects of everyday life, reshaping the experiences of individuals in profound ways. Faster content downloads coupled with remarkably low latency create a seamless and rapid access to digital content. This heightened speed and responsiveness elevate the quality of online interactions.
Additionally, 5G’s capabilities empower users to effortlessly connect multiple devices concurrently. This paves the way for immersive applications such as augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), enhancing experiences like headgear-assisted virtual collaboration. Furthermore, the Internet of Things (IoT) finds a robust partner in 5G, enabling applications like field sensors that gather and transmit data from outdoor with unprecedented efficiency. The convergence of 5G with Artificial Intelligence (AI, e.g.: ChatGPT) catalyzes innovation in revolutionizing automated systems.
A standout feature of 5G is the virtually instantaneous access to cloud services. This enables a gamut of experiences, from multiplayer cloud gaming that thrives on real-time interaction to shopping experiences enhanced by real-time video translation. The collaboration landscape is also elevated, allowing individuals to engage in seamless real-time collaboration across distances.
Key Application Areas of 5G:
5G technology finds its major applications in three key areas: enhanced mobile broadband, mission-critical communications, and Internet of Things (IoT) connectivity. These applications stem from these fundamental use cases, and delving deeper, we can explore the following specific application areas:
1. Improved Entertainment and Multimedia Across Devices
Indeed, 5G’s capabilities hold the potential to revolutionize the entertainment industry, offering a high-definition virtual world accessible through mobile devices. The technology facilitates high-speed streaming of 4K videos with impeccable visual quality and crystal-clear audio, enabling seemingly live events and providing uninterrupted access to HD TV channels. These advancements translate into a vastly enhanced entertainment experience.
Furthermore, 5G’s impact extends to the realm of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR), where the demand for HD video and low latency is paramount. The technology can work wonders in delivering incredible virtual experiences, enabling immersive environments with minimal lag. This becomes particularly evident in HD virtual reality games, where 5G’s capabilities contribute to a smoother and more seamless online gaming experience. As a result, 5G’s influence reverberates through entertainment, enhancing both passive and interactive content consumption.
2. Smart Home and Smart City Development
Smart Homes illustrate the seamless automation of our daily needs, intuitively responding to our preferences. This includes tasks like activating or deactivating home appliances even when we’re away. Security cameras play a pivotal role as well, surveilling and safeguarding our homes through real-time angle adjustments and event capture.
Expanding this concept on a larger scale leads us to the realm of smart city applications. These applications encompass a diverse spectrum of functionalities such as efficient traffic management, real-time roadside assistance, dissemination of weather updates and local information, intelligent street lighting, precision utility metering, crowd control, and bolstered city safety and security measures. Crucially, the foundation enabling these applications to operate smoothly and dependably is rapid network connectivity, notably provided by technologies like 5G.
3. Logistics and Tracking of Goods
Logistics revolves around the dynamic movement of assets, making real-time monitoring a critical aspect. In this context, low latency becomes essential, and 5G emerges as a transformative solution with its remarkably swift response times. This quality positions 5G as an ideal enabler for enhancing various aspects of logistics operations.
By harnessing 5G’s capabilities, logistics processes like goods tracking, fleet management, staff scheduling, and reporting can be streamlined to operate with efficiency in real time. The ability of 5G to seamlessly connect multiple devices simultaneously renders it exceptionally well-suited for central management systems, enabling the concurrent oversight of numerous fleets in transit.
Furthermore, the integration of smart tracking devices equipped with GPS ushers in a new era of precision. These devices offer accurate monitoring of crucial factors such as temperature, shock, light exposure, and humidity in near real time. This level of monitoring serves to significantly reduce the risks associated with theft or the misplacement of valuable items.
4. Industrial IoT Applications Supporting Industry 4.0
The landscape of industrial applications is undergoing a rapid transformation driven by automation. Processes that have existed for nearly a decade are now seamlessly automated and operating with remarkable efficiency. This revolution in automation is underpinned by cutting-edge Internet of Things (IoT) applications, which are built upon the foundation of intelligent wireless technologies like 5G.
The ultra-fast and responsive nature of 5G networks contributes significantly to this industrial evolution. It injects speed and efficiency into every facet of the industrial process. This includes transformative practices like predictive maintenance, where data-driven insights anticipate maintenance needs before issues arise. Process tracking becomes more granular and insightful, yielding greater precision and control. Smart packing solutions optimize the utilization of resources, reducing waste and inefficiencies. Energy management is elevated to a new level of sophistication, enhancing sustainability efforts.
5. Smart Farming and Livestock Monitoring for Better Productivity
Farming stands as another domain ripe for transformation through the integration of sensors, RFIDs, and GPS technology. The advent of smart farming brings forth a paradigm shift, enabled by real-time data acquisition. This data encompasses crucial factors such as soil temperature, water content, instances of insecticide attacks, and the precise location of livestock. The beauty of this system lies in its capacity to facilitate remote real-time management of these aspects, even from considerable distances.
In practical terms, smart farming has multifaceted applications. It streamlines irrigation practices through data-driven insights, optimizing water usage and enhancing sustainability. Access control takes on a new dimension, as technology allows for precise oversight of farm areas and livestock locations. Furthermore, the implementation of smart farming techniques contributes to efficient energy management, reducing waste and resource consumption.
The convergence of wireless connectivity, exemplified by innovations like 5G, marks a transformative step forward in the agricultural sector. It not only enhances productivity but also aligns farming practices with sustainability goals, bolstering efficiency while minimizing environmental impact.
6. Healthcare and Mission-critical Applications
The potential of 5G in the healthcare sector is nothing short of transformative. It opens the door for a doctor situated in one part of the world to perform critical medical procedures on patients located in distant regions, effectively overcoming geographical barriers. Given the swift reactivity of the human body, real-time execution of medical procedures can often be a matter of life and death. Here, 5G’s low latency and rapid communication capabilities can play a pivotal role in ensuring the precision and success of such operations.
Moreover, 5G holds immense promise for patients with chronic medical conditions. Smart devices equipped with this technology can continuously monitor a patient’s health parameters in real time. This data can then be relayed to healthcare providers, allowing for timely intervention in the event of health deterioration or progress. This facet of 5G-powered healthcare ensures that patients receive proactive and targeted medical attention.
One of the remarkable applications of 5G lies in high-definition medical imaging technologies, like MRI scans, which generate data files exceeding 1GB. 5G’s exceptional data transfer speed makes it possible to transmit these sizable files in a matter of seconds, fostering more rapid and precise diagnosis.
7. Autonomous Driving of a Car or a Shipping Truck
Prior to the advent of 5G, the realization of truly autonomous driving was hindered by the need for real-time decision-making by onboard vehicle computers. These decisions heavily rely on continuous connectivity while on the road. This is where the power of high-performance wireless networks, particularly 5G, comes into play. The low latency offered by 5G technology is a game-changer, rendering autonomous driving both safer and more feasible.
Autonomous vehicles, whether cars or trucks, can leverage the capabilities of 5G to establish communication with their surroundings. This encompasses interactions with nearby objects, traffic signals, and other vehicles sharing the road. The higher level of real-time intercommunication facilitated by 5G is pivotal in avoiding potential collisions and ensuring passenger safety.
Key Benefits it Offers to the Industry:
According to findings from Accenture, the implementation of 5G is projected to yield beneficial effects across industries, driving increased efficiency and fostering the development of fresh products and avenues for generating revenue. Presented below is a concise overview:
| Manufacturing | Healthcare | Automotive | Agriculture |
| 1. 20% to 30% overall productivity gains 2. 50% improvement in assembly efficiency 3. 20% increase in asset life 4. 90% defect detection | 1. 30% cost savings in transition to remote-home-based models | 1. 80% reduction of vehicle accidents 2. USD 3.6 Billion savings in repair costs 3. 25% reduction in traffic | 1. Improved connectivity and digitization to yield up to 25% increased productivity 2. 30% decreased inputs, 20% decreased costs 3. 15% increased crop yields |
Availability of 5G Around the World:
As of January 2023, the global count of commercial 5G networks stood at 229, accompanied by a remarkable selection of over 700 5G smartphone models accessible to consumers. Insights from GSMA Intelligence forecast a doubling of 5G connections between 2023 and 2025. This growth trajectory will be fueled by ongoing technological advancements and the accelerated launch of new 5G networks in more than 30 nations exclusively within the year 2023.
Additionally, as per Viavi Solutions’ projections indicate that by March 2023, 5G networks will be operational in 47 out of the world’s 70 largest economies measured by GDP. This underscores the rapid expansion of 5G technology across a global landscape, marking a significant milestone in its widespread adoption.
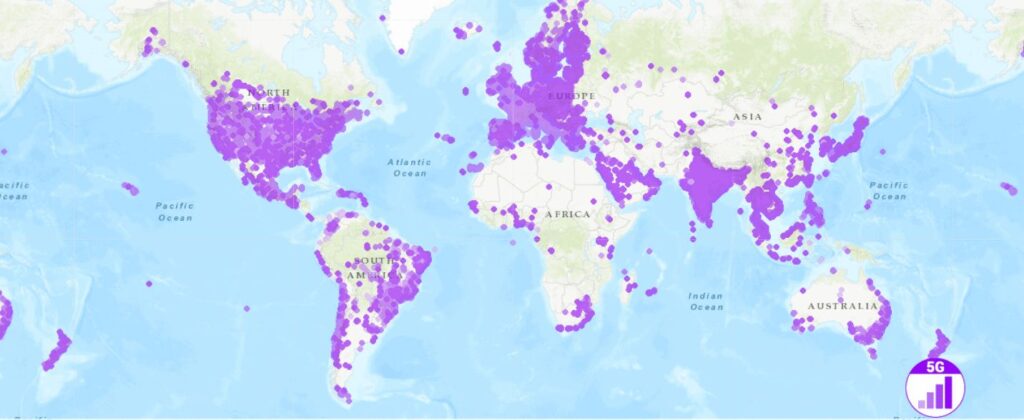
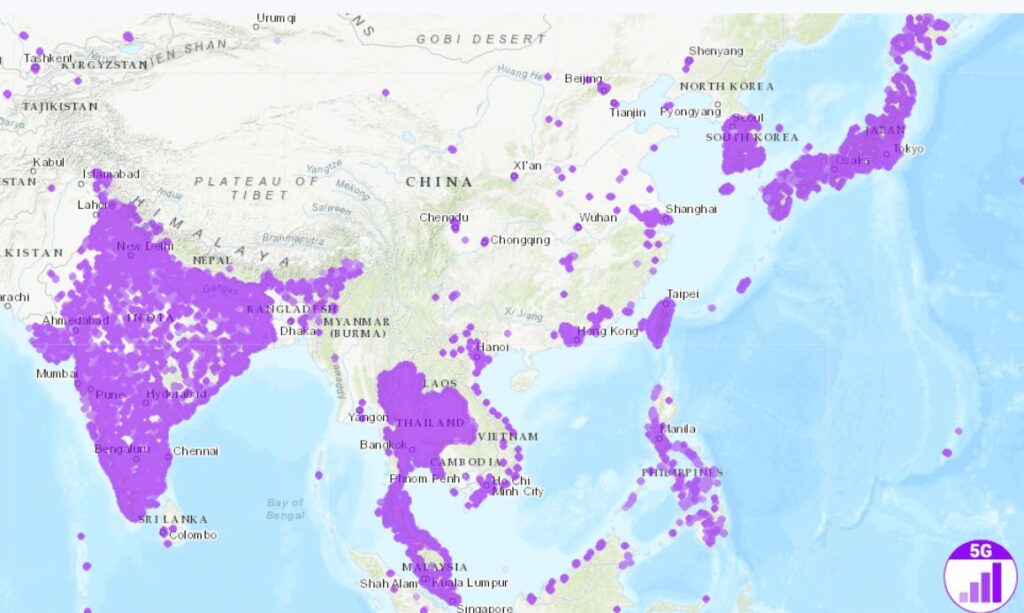
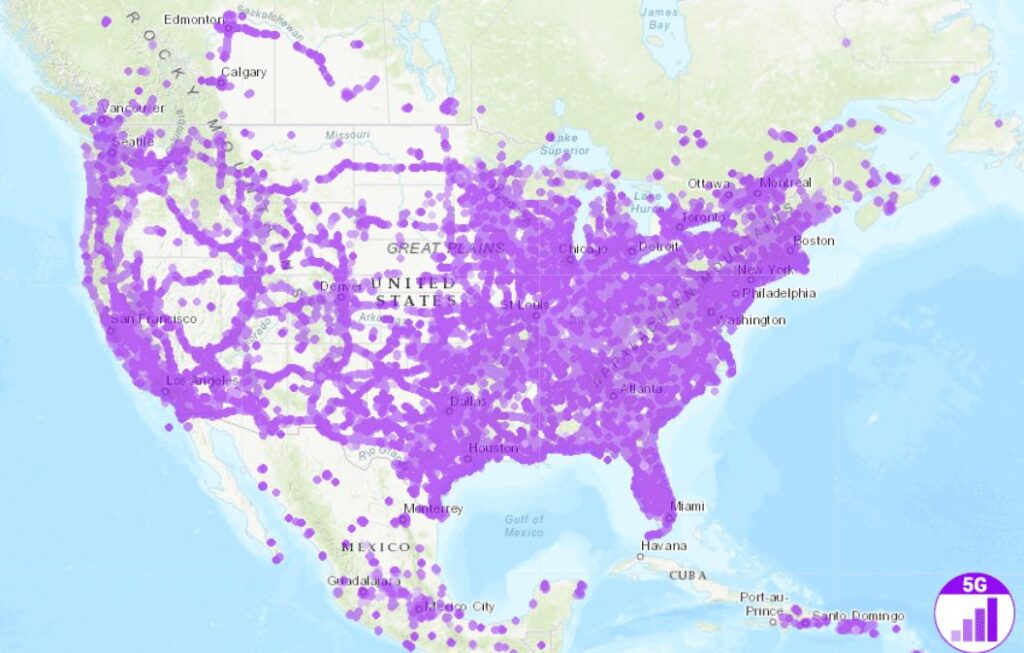
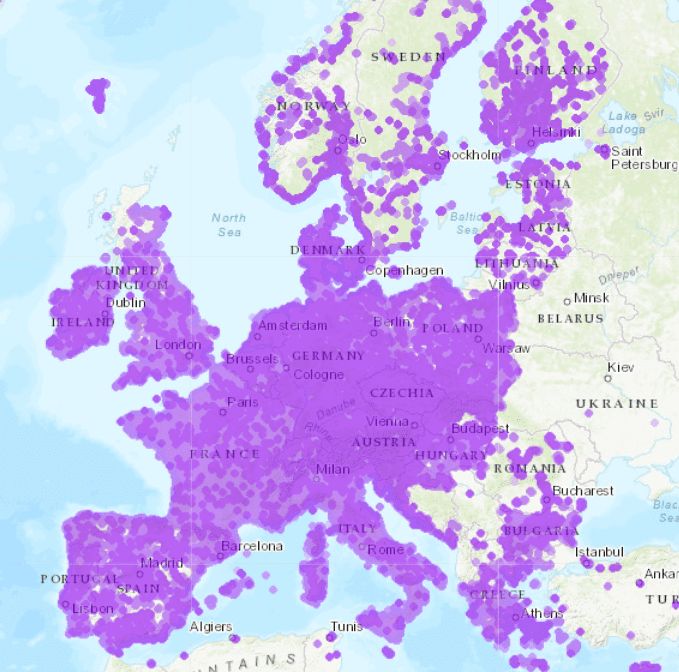
Source: nPerf
Key Developments in 5G in the Top-5 Economies
United States:
As per an expectation, by 2030, the 5G economy is poised to make an astounding contribution of USD 1.7 Trillion to the economic growth of the United States, concurrently generating an impressive 4.6 million jobs.
As of 2022, the reach of 5G networks had already expanded extensively across the United States, with approximately 95% of the population gaining access to these networks. Furthermore, nearly 80% of the population enjoyed access to networks capable of delivering download speeds of up to 200 Mbps, up to ten times faster than 4G.
The commitment of major wireless operators to advancing their networks is evident from the significant investments made. The year 2021 witnessed an investment of around USD 35 Billion in wireless networks, translating to approximately USD 105 per capita. This marked increase showcases the industry’s dedication to progress, especially when compared to the USD 95 per capita investment recorded in 2019.
China:
China has set ambitious targets for the adoption of 5G technology, aiming to achieve 1 billion 5G subscribers by 2025 and a overwhelming 1.6 billion by 2030. Impressively, by 2022, China had already established a remarkable 2.3 million 5G base stations, with nearly 887,000 of these stations built just within that year.
The anticipated impact of 5G on the Chinese economy is substantial. Projections suggest that by 2030, 5G will contribute a noteworthy USD 290 Billion to the economy, with its benefits permeating through various industries.
As of 2022, Mainland China solidified its position as the world’s largest 5G market, commanding over 60% of the global 5G market share. China plans to phase out legacy networks within the country by 2025, underscoring the nation’s commitment to advancing its digital infrastructure.
Predictions indicate that by 2023, 5G will account for around 45% of all mobile connections in the country. This figure is expected to surge to an impressive 88% by 2030. In parallel, 4G connections are projected to decrease to 55% by 2023 and further to 12% by 2030, highlighting the swift transition toward 5G adoption.
Japan:
Japan is aiming for an extensive coverage of 5G networks, with a target to serve 99% of its population with this technology by 2030. This commitment to widespread connectivity is reflected in the projected increase in 5G network density, which is expected to rise from 153% in 2021 to 154% by 2025.
Simultaneously, the adoption of 5G smartphones is poised to see substantial growth. The percentage of users adopting 5G smartphones is anticipated to climb from 71% in 2021 to a promising 81% by 2025. Moreover, the penetration of 5G subscribers in Japan is projected to rise from 87% in 2021 to 88% by 2025, further underlining the swift pace of adoption.
To fuel this expansion, major Japanese telecom players are earmarking significant investments. By 2025, NTT Docomo has plans to allocate over USD 7 Billion to extend its network to encompass 97% of the country’s populated areas. Similarly, KDDI aims to invest more than USD 4 Billion to reach 93% of the population, while Softbank and Rakuten Mobile intend to spend over USD 1.9 Billion (to reach 64% of the population) and USD 1.8 Billion (to reach 56% of the population) respectively to achieve extensive coverage for their networks.
Germany:
In the year 2023, approximately 85% of locations in Germany have embraced the coverage of 5G networks. Prominent urban centers like Berlin, Hamburg, and Bremen enjoy comprehensive 5G network coverage. Meanwhile, the expansion of coverage is still ongoing in certain territorial states.
Deutsche Telekom’s 5G network has made substantial progress, encompassing 94% of the total population in Germany by 2023. Vodafone has achieved an 80% household coverage with its 5G network, and Telefonica (O2) has reached 75% coverage, highlighting the efforts of these major telecom operators in enhancing connectivity and technological reach across the nation.
India:
India has taken the global stage by surprise with its swift adoption of 5G technology, outpacing other nations in the speed of implementation. As of 2022, India reached around 31 million 5G subscribers, a figure projected to soar to 300 million by 2025 and an overwhelming 690 million by 2028. This robust adoption is anticipated to account for approximately 57% of the country’s mobile subscriptions.
The trailblazers in India’s 5G journey are Reliance Jio and Bharti Airtel, emerging as leaders by offering value-added “True 5G” and “5G Plus” services to users through a phased approach. Jio is striving to complete its 5G rollout by 2023, while Airtel aims for full implementation by March 2024.
In 2023, nearly 35% of the 170 million smartphones in the country are 5G-enabled, giving a significant boost to 5G streaming services. This growing number is expected to contribute to an increase in monthly data consumption, projected to rise from approximately 20GB in 2023 to 30GB by 2025.
Investments have been substantial in establishing India’s 5G infrastructure. Reliance Jio, for instance, has invested a hefty USD 25 Billion, creating a network that includes “True 5G” towers (Stand Alone 5G or SA 5G) that operate independently, without relying on support from the 4G LTE network. In contrast, Bharti Airtel employs the C-band spectrum and delivers 5G through a Non-Standalone Mode (NSA 5G).











7 thoughts on “Unveiling the Power of 5G Network Technology and Its Future”